
Peer review is the unbiased assessment of your research article by experts in the field. Peer review is an academic journal’s quality control measure and a helpful input source. You can use the feedback to make changes to your manuscript before publication.

Step 1: Submission
Writers get ready for their work to be assessed by professionals in the industry. They select whether the peer review will be open, double-masked, or blind. Whereas double-masked reviews withhold the identities of both authors and reviewers, anonymous reviews reveal the identities of all authors.
Comprehending these choices guarantees a seamless submission procedure. Before submitting their work via an online portal, authors ensure it is checked and formatted per the journal’s criteria. A well-written paper improves the likelihood of a favorable peer review.
Step 2: Editorial Review
In the process of academic publishing, submissions are reviewed by editors. Journal editors do an initial assessment of the quality and relevancy of the material. This critical stage decides whether the work gets accepted for peer review or rejected.
Editors consider criteria conformity, general quality, and compatibility with the journal’s scope. This stage saves time and resources by guaranteeing that only papers with publishing potential move on to peer review. A thorough editorial review prepares the work for in-depth peer review.
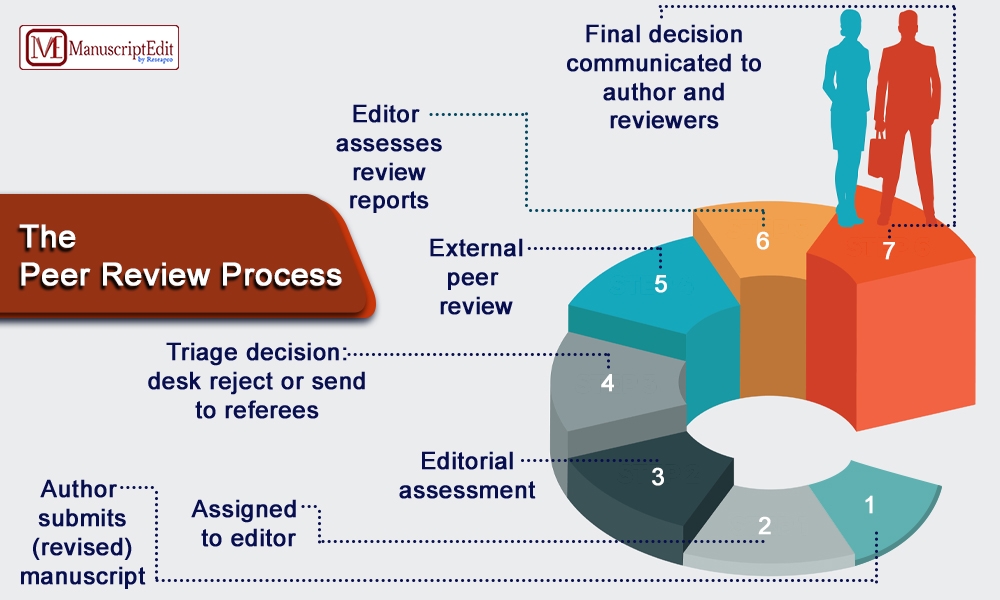
Step 3: Peer Review
Expert reviewers are selected based on their expertise in the relevant field. These reviewers carefully evaluate the manuscript’s quality, validity, and importance. Reviewers consider the research strategy, methodology, data analysis, findings, and conclusions to ensure the study meets the highest standards of academic rigor.
They point out weaknesses, provide solutions, and advise accepting or rejecting changes. Only top-notch research is published thanks to the peer review process and the helpful criticism that authors receive on their work.
Step 4: Revision
Authors thoroughly consider every feedback and make adjustments, explanations, and enhancements. Following adjustments, the paper is resubmitted with a thorough explanation of how the changes meet the reviewers’ concerns and a detailed response to their remarks.
To support their writing, authors may additionally include more information or justifications. By going through this revision process, you can be sure that the final paper will match the high requirements of academic publishing and will be thoroughly tested, improved, and refined.
Step 5: Re-evaluation
Reviewers and Editors evaluate how much the author has improved the article and addressed the earlier issues. Reviewers offer more commentary, and editors assess the quality and applicability of the edits. Based on this assessment, the editor renders a final decision: acceptance, rejection, or additional rewriting. The manuscript goes to publication if it is accepted.
The author may reapply or consider publishing elsewhere if their submission is denied. Before concluding, the author addresses any remaining concerns, such as if more rewriting is necessary. This stage guarantees that the published material satisfies the highest requirements.
Conclusion
Understanding peer review can help readers and writers trust the process and contribute more successfully, producing high-caliber research that benefits society and advances knowledge.
