 Demystifying Footnotes and Endnotes: Exploring Their Purpose and Distinctions:
Demystifying Footnotes and Endnotes: Exploring Their Purpose and Distinctions:
Introduction:
In academic and professional writing, proper citation and referencing are crucial to maintain the integrity of the work and give credit to the sources used. Footnotes and endnotes are two common methods employed for this purpose. This blog will explore the purpose and differences between footnotes and endnotes, learn how to cite them, discuss their advantages, and understand why they are essential in scholarly writing.

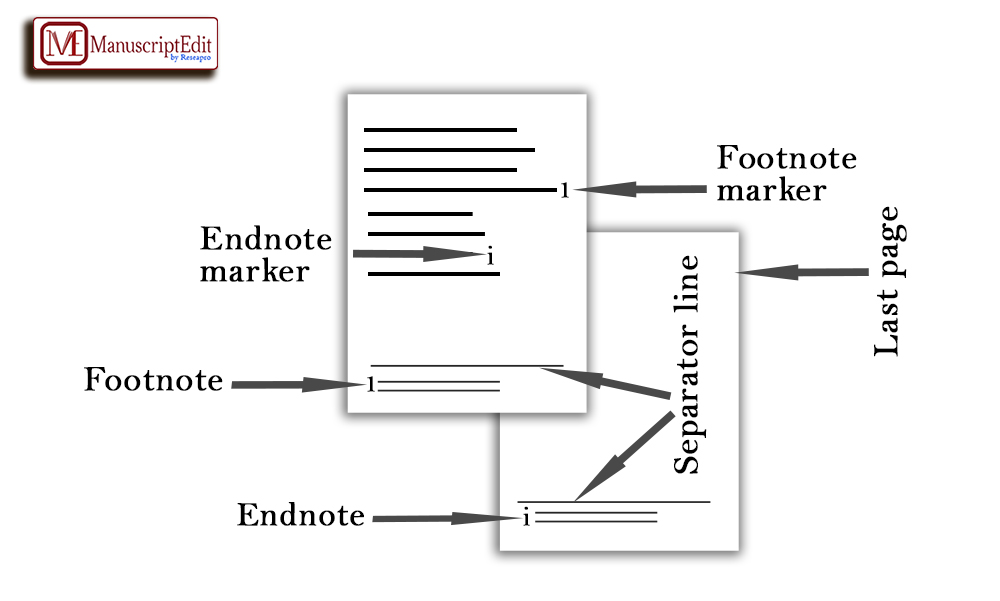
Fig 1. Figure depicting footnotes and endnotes.
- Footnotes vs. Endnotes: Footnotes and endnotes both offer additional information or citations within documents. Their primary distinction lies in placement. Footnotes are typically added after paragraph breaks, while endnotes should follow them immediately at the bottom.
- Footnotes: Footnotes are placed at the bottom of a page directly below its main content and used to provide explanations, references, or additional comments without disrupting its flow.
- Endnotes: Unlike footnotes, endnotes appear at the end of a document after all major sections and appendices have been reviewed and completed. They perform the same function but in an easier-to-digest form.
- Purpose of Footnotes and Endnotes: Both footnotes and endnotes serve several essential purposes in academic and professional writing:
- Attribution: They allow writers to provide proper credit to the original sources, avoiding plagiarism.
- Additional Information: Footnotes and endnotes allow writers to elaborate on certain points or provide background information without cluttering the main text.
- Source Verification: By including references in footnotes or endnotes, readers can easily verify the sources and delve deeper into the topic if desired.
- How to Cite Footnotes and Endnotes: Citing footnotes and endnotes correctly is essential to maintain the work’s credibility. The citation format may vary depending on the style guide (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). However, a general format for citing a book in a footnote/endnote is as follows:
- Footnote: Author’s First and Last Name, Book Title (Place of Publication: Publisher, Year), page number.
- Endnote: Same as the footnote, but collected at the end of the document.
- Advantages of Using Footnotes: Footnotes offer some distinct advantages in scholarly writing:
- Enhanced Readability: Footnotes keep the main text clean and uncluttered, providing a seamless reading experience.
- Easy Reference: Readers can quickly check the sources and additional information without flipping to the end of the document.
- Supplementary Content: Footnotes allow writers to add context or digress from the primary topic without losing the flow of the main content.
Conclusion
In conclusion, footnotes and endnotes are valuable tools in academic and professional writing, aiding in proper citation, source verification, and information supplementation. The choice between footnotes and endnotes often depends on the writer’s preference and the project’s specific requirements. (https://idepfoundation.org/) By understanding their purposes and differences, writers can use footnotes and endnotes effectively to enhance the quality and credibility of their work.
To explore the art of scholarly writing and academic publishing, visit manuscriptedit.com. Stay informed and refine your writing skills to become a successful author or researcher.
[credit-prerana]
